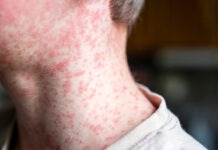
Case scenario
Mrs Ng comes into the pharmacy with her 6-year-old son Max after seeing the doctor. Mrs Ng was very worried after Max developed a sore mouth and small vesicles on the soles of his feet and palms of his hands. She tells you the doctor said Max has hand, foot and mouth disease. She remembers the doctor discussed keeping Max from school, but she can’t recall for how long. Mrs Ng requests pain relief for Max and asks if you have any further advice about this condition.
After reading this article, pharmacists should be able to:
Competency standards (2016) addressed: 1.1, 1.4, 1.5, 3.1, 3.2 Accreditation number: CAP2408DMJM Accreditation expiry: 31/7/2027 |
Already read the CPD in the journal? Scroll to the bottom to SUBMIT ANSWERS.
Introduction
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is a generally mild, but contagious, viral infection caused predominantly by coxsackieviruses.1–4 It is different to foot and mouth disease, which occurs only in animals.4 HFMD usually affects infants and children, but may occur in adults.2,5 Outbreaks are more common in summer and early autumn, although they can also occur during winter.5–9 The most characteristic presentation is lesions that d
THIS IS A CPD ARTICLE. YOU NEED TO BE A PSA MEMBER AND LOGGED IN TO READ MORE.

 Professor Margie Danchin[/caption]
Professor Margie Danchin[/caption]
 Dr Peter Tenni[/caption]
Dr Peter Tenni[/caption]
 How should we deprescribe gabapentinoids, according to the Maudsley Deprescribing Guidelines[/caption]
How should we deprescribe gabapentinoids, according to the Maudsley Deprescribing Guidelines[/caption]


 Pharmacists have always prescribed, but they have the potential to prescribe much more
Pharmacists have always prescribed, but they have the potential to prescribe much more